NATURAL REGIONS
Most of the population live in the low coastal plain
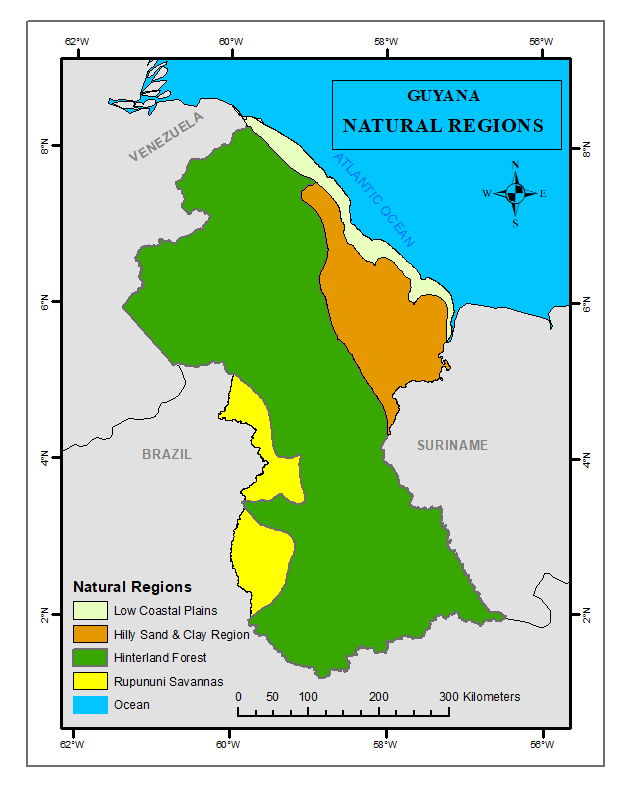
Guyana can be divided into four main Natural Regions:
- The Low Coastal Plain: The Low Coastal Plain is a narrow belt that borders the Atlantic Ocean. It is approximately 9,120 square kilometers in area and 1 – 3 meters below mean sea level. The length of the Atlantic Coast is approximately 440 kilometers or 270 miles.The coastal plain is known for its silty clay, pegasse and sandy soil, which is used for planting fruits, vegetables, rice, sugar and coconut.
- The Hilly Sand and Clay Region: The Hilly Sand and Clay Region is mostly covered in scrub (low) to medium height vegetation. It is located south of the Low Coastal Plain, with an area of approximately 28,920 square kilometers. The Hilly Sand and Clay Region is known for its bauxite mines, red and white clay and hills ranging 30 – 122 meters in height. Its main resources and economic activities are bauxite mining, logging and stone quarrying.
- The Hinterland Forest: The Hinterland Forest is the main source of forest wealth for Guyana. It makes up about 73% of the country’s land mass with an area of approximately 156,450 square kilometers. The region is known for its mountain ranges (Kanuku, Pakaraima, Imataka and Acarai), dense forest timber and rich gold and diamond deposits.
- The Rupununi Savannah: The Rupununi Savannahs were named after the Rupununi River situated in the South-West Region of Guyana. The forested Kanuku Mountains divide the area into two – the North and South Savannahs. The vegetation consists of mostly grassland, scrub and low trees with hills. The main economic activities are cattle ranching, balata bleeding and farming.